


Next: Experimental setup
Up: Calculation of eddy currents
Previous: Boundary conditions
Contents
FEMM
The finite element package FEMM by David Meeker [3] provides a complete set of tools for solving static and low frequency 2D or axisymmetric problems in electrodynamics. Like any typical FE package it consist of the following three parts:
Preprocessor
The preprocessor (femme.exe) is a CAD-like program for defining the geometry of the problem, material properties, mesh densities and boundary conditions. The finite element mesh can be created and viewed. Figure 1 shows a snapshot of the preprocessor with a model of the single turn coil (cf. section  ). The horizontal axis is the r -axis and the vertical axis is the z -axis. The small dot in the middle on the left border, which is the symmetry axis, is the sample and to its right the cross section of the single turn coil is visible. The semi-circle denotes the boundary, where asymptotic boundary conditions are applied. In all following figures this ( r >0, z) plane with the asymptotic boundary will be displayed.
). The horizontal axis is the r -axis and the vertical axis is the z -axis. The small dot in the middle on the left border, which is the symmetry axis, is the sample and to its right the cross section of the single turn coil is visible. The semi-circle denotes the boundary, where asymptotic boundary conditions are applied. In all following figures this ( r >0, z) plane with the asymptotic boundary will be displayed.
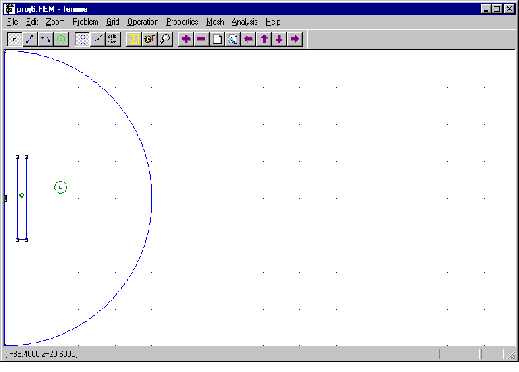
Figure  : User interface of the preprocessor
: User interface of the preprocessor
Solver
The solver (fkern.exe) reads the information defined during the preprocessing step and solves Maxwell's equations.
Postprocessor
The postprocessor (femmview.exe) displays the results as density and contour plots. In addition the user can inspect the solution at any point, plot interesting results in graphs and calculate certain integrals.
2D simplifications
In general, the magnetic vector potential is a 3D vector with three non-vanishing components. However, in 2D planar and axisymmetric cases two of these components are zero. Only the "out of plane" component is non-zero. The vector potential approach has the advantage, that only one equation (8) or (11) has to be solved. The magnetic field and the magnetic induction can be deduced by differentiating the vector potential. In addition, (8) is an elliptic partial differential equation. This is a well known and thoroughly studied type, which occurs in many engineering problems.
Axisymmetric problems
In axisymmteric problems the magnetic vector potential must vanish at 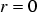 . Thus, we do not have to define any other Dirichlet boundary conditions, if
. Thus, we do not have to define any other Dirichlet boundary conditions, if 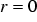 is part of the domain boundary.
is part of the domain boundary.
Program test
The finite element package FEMM has been tested by calculating the magnetic field of a single turn coil with constant current. The results can easily be compared with the analytic solution. proj7.fem
inner diameter: 5 cm
coil area S: 78,54 cm2
cross section: 0.2(0.2 cm2 = 0.04 cm2 = 4e-6 m2
current density: 1 MA/m2
total current: 4 A
The magnetic induction B at 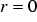 in the centre of the coil is given by [4]
in the centre of the coil is given by [4]
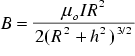 (
( 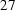 )
)
With the data given above we get B = 5.0265e-5 T. (The cross section of the coil has been neglected.)
With FEMM we get the following results:
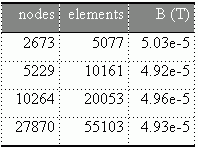
Table  : FEMM results for FE meshes with different density
: FEMM results for FE meshes with different density
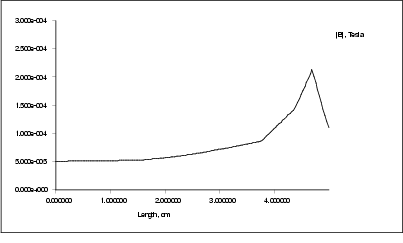
Figure  : Induction in radial distance from the symmetry axis
: Induction in radial distance from the symmetry axis



Next: Experimental setup
Up: Calculation of eddy currents
Previous: Boundary conditions
Contents
© 1999
Werner Scholz
werner.scholz (at) tuwien.ac.at
 ). The horizontal axis is the r -axis and the vertical axis is the z -axis. The small dot in the middle on the left border, which is the symmetry axis, is the sample and to its right the cross section of the single turn coil is visible. The semi-circle denotes the boundary, where asymptotic boundary conditions are applied. In all following figures this ( r >0, z) plane with the asymptotic boundary will be displayed.
). The horizontal axis is the r -axis and the vertical axis is the z -axis. The small dot in the middle on the left border, which is the symmetry axis, is the sample and to its right the cross section of the single turn coil is visible. The semi-circle denotes the boundary, where asymptotic boundary conditions are applied. In all following figures this ( r >0, z) plane with the asymptotic boundary will be displayed.

 : User interface of the preprocessor
: User interface of the preprocessor
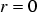 . Thus, we do not have to define any other Dirichlet boundary conditions, if
. Thus, we do not have to define any other Dirichlet boundary conditions, if 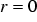 is part of the domain boundary.
is part of the domain boundary.
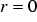 in the centre of the coil is given by [4]
in the centre of the coil is given by [4]
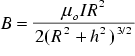 (
( 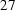 )
)

 : FEMM results for FE meshes with different density
: FEMM results for FE meshes with different density

 : Induction in radial distance from the symmetry axis
: Induction in radial distance from the symmetry axis