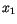 ,
, 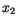 , ... and take some functions
, ... and take some functions
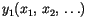 ,
,
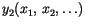 , ... of it. The joint probability distribution of the
, ... of it. The joint probability distribution of the 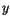 's is given by the fundamental law of probability
's is given by the fundamental law of probability
If the random numbers are required to obey a certain distribution function, the transformation method [46] can be applied. By transforming uniformly distributed random numbers, random variables with any probability distribution, given that the indefinite integral is known and invertible, can be generated.
Suppose, we generate uniform deviates 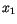 ,
, 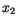 , ... and take some functions
, ... and take some functions
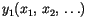 ,
,
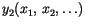 , ... of it. The joint probability distribution of the
, ... of it. The joint probability distribution of the  's is given by the fundamental law of probability
's is given by the fundamental law of probability
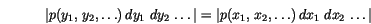
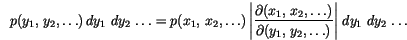
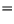
The Box-Müller method uses this technique to generate random deviates with normal (Gaussian) distribution,
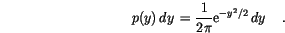
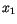 and
and 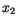 on
on 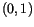 and two quantities
and two quantities 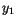 and
and 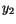 is given by
is given by
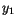 |
 |
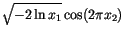 |
(7.12) |
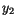 |
 |
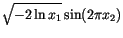 |
(7.13) |
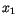 |
 |
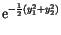 |
(7.14) |
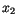 |
 |
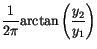 |
(7.15) |
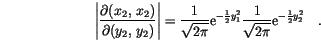
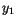 alone and a function of
alone and a function of 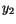 alone, each
alone, each 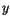 is an independent Gaussian random variable.
is an independent Gaussian random variable.
The implementation of these algorithms in the http://beta.ulib.org/webRoot/Books/Numerical_Recipes/Numerical Recipes [46] and the http://www.nag.co.uk/NAG library [47] have been used for the implementation of the stochastic thermal field.