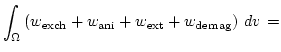 |
(3.1) | ||
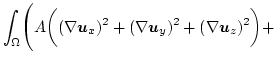 |
|||
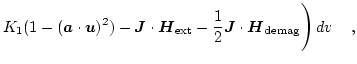 |
The total Gibbs free energy is given by [33,34]
In thermodynamic equilibrium a micromagnetic system tries to reach a state with minimum total energy.
The aim of micromagnetic theory is to find the magnetic polarization in equilibrium. Brown proposed a variational method [33], which is based on the calculation of the variational derivative of the total energy with respect to the magnetic polarization. In equilibrium (in an energy minimum) the coefficients of the linear term vanish for any variation
![]()
| (3.3) |
Thus, in equilibrium the magnetic polarization
![]() is parallel to an ``effective field''
is parallel to an ``effective field''
| (3.6) |
Since any contribution parallel to the polarization
![]() does not add to the torque, it does not make any difference if the magnetic field
does not add to the torque, it does not make any difference if the magnetic field
![]() or the magnetic induction
or the magnetic induction
![]() is used for the effective field.
is used for the effective field.